How to Edit Hosts File on Windows Using Command Prompt
In this guide, I’ll show you how to edit the hosts file in Windows 10 and Windows 11 using Command Prompt.
Normally, when you want to modify the hosts file, you open Notepad as an administrator and browse through the file system to locate it. But using the command-line method can be faster and more efficient.
Step 1: Open Command Prompt as Administrator
The first thing you need to do is start Command Prompt as administrator.
In Windows 10, Windows 11 or Server 2025 right-click the Start button and select Terminal (Admin).
This ensures you have the necessary privileges to edit and save the hosts file.
Step 2: Go to the Hosts File Directory
Next, navigate to the folder where the hosts file is stored. Type the following command and press Enter:
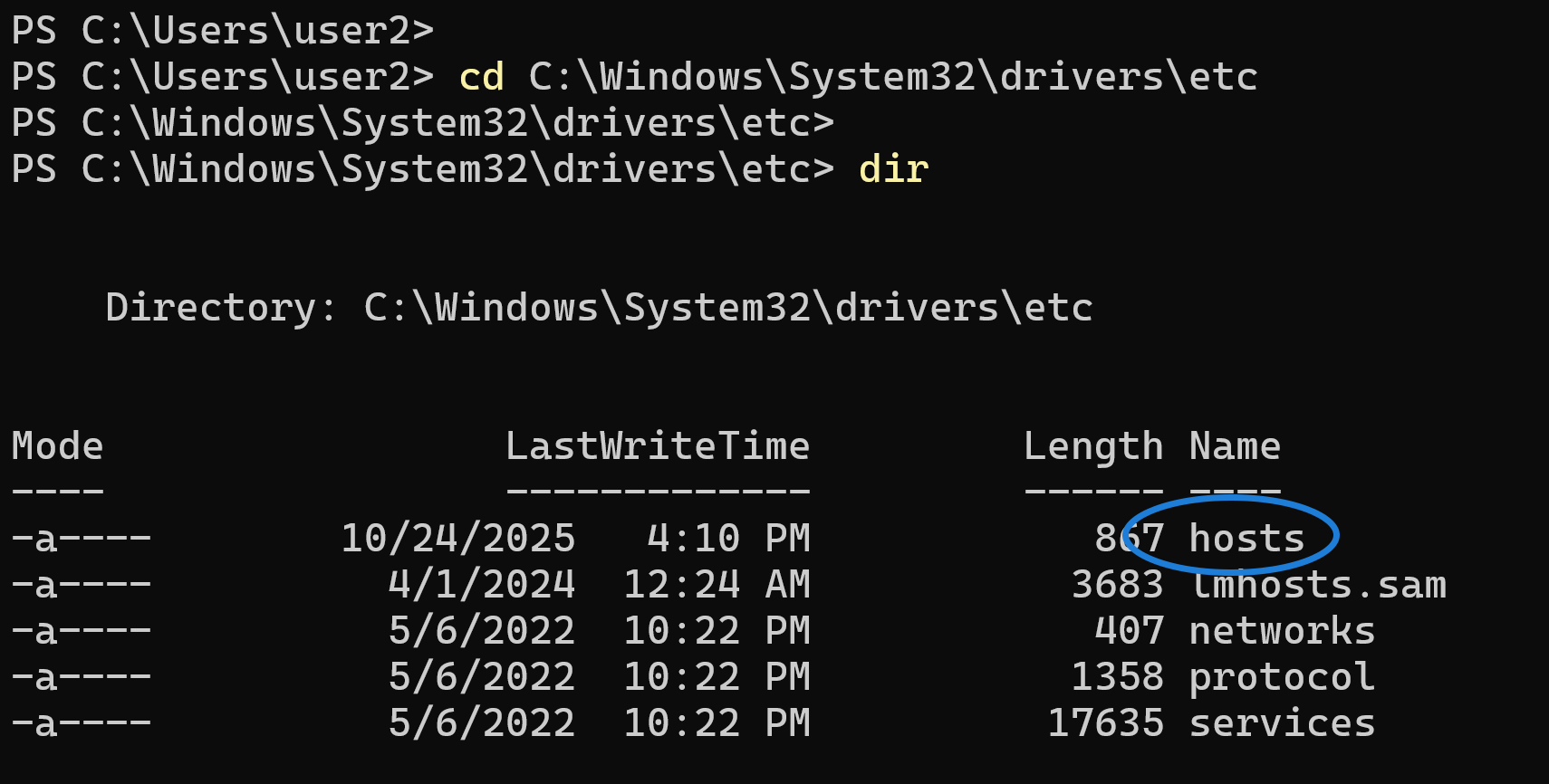
cd C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etcThis is the default location of the hosts file in all modern Windows versions. To confirm, you can list the files in the directory by typing:
dirYou’ll see a file named hosts — that’s the file we need to edit.
Step 3: Open the Hosts File in Notepad from CMD
Now, open the hosts file directly from Command Prompt by typing:
notepad hostsThis command launches the hosts file in Notepad. Because the terminal was opened as administrator, Notepad will also run with administrator privileges — allowing you to edit and save changes without any permission issues.
Step 4: Add or Modify Host Records
Inside the file, you can add new host entries or modify existing ones.
Each record should follow this format – IP address followed by domain name.
Example
192.168.1.10 example.comYou can add as many host records as you need, each on a separate line, for different IP addresses.
192.168.1.10 example.com www.example.com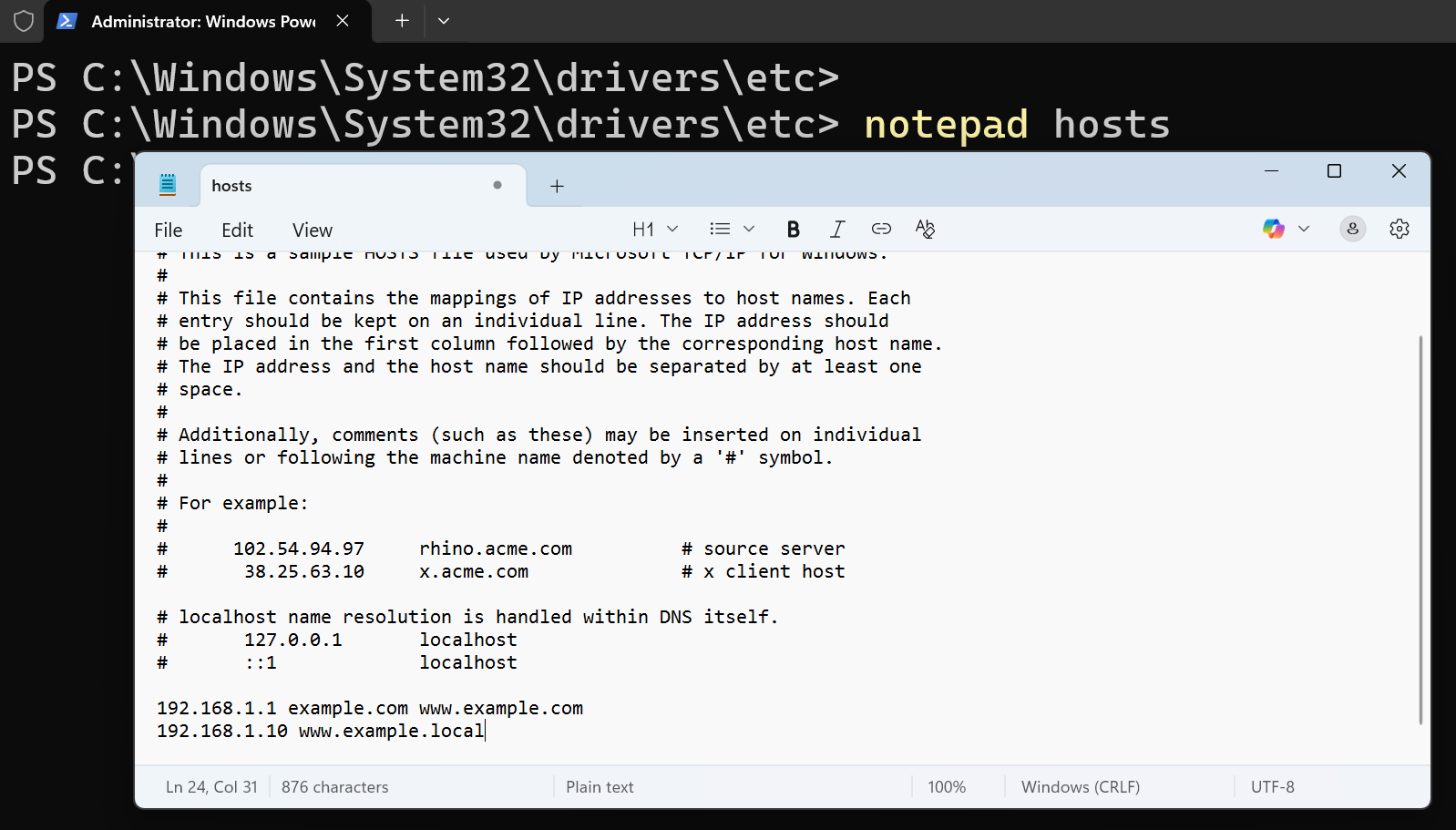
Step 5: Save the File
After you finish editing, simply save the file from Notepad. Since you opened Command Prompt as administrator, you shouldn’t get any “Access Denied” or permission errors.
That’s it — you’ve successfully edited the hosts file in Windows 10 or Windows 11 using Command Prompt.
Why Use Command Prompt to Edit the Hosts File?
- No need to manually navigate to the file in File Explorer
- Faster than opening Notepad through menus
- Automatically grants administrator privileges
- Works the same on both Windows 10, Windows 11, and Server 2025.