How to Keep Ubuntu Docker Containers Running (Fix Exited Containers)
In this tutorial, you will learn how to start an Ubuntu Docker container and keep it running in the background. A common issue beginners face is that a container stops immediately after it is started. We will explore why this happens and the correct ways to keep operating system containers active.
Why Does My Ubuntu Container Stop Immediately?
Normally, if you start a new container using docker run -d ubuntu, it will create the container, but it won't stay active. If you run the docker ps command (the tool used to see running containers), the list will be empty. Using docker ps -a will show the container, but the status will be Exited.

The reason is simple: Docker containers only stay alive if there is a primary service or process running inside. Since operating system containers like Ubuntu and Debian do not have services running by default, the container exits immediately after it is created because it has no task to perform.
Method 1: Using the -dt Flags (Recommended)
The most efficient way to keep an operating system container running in the background is to attach a pseudo-terminal. You can do this using the -t option.
The Command:
docker run -dt ubuntuBy using -dt (detached and tty), Docker starts the container in the background and keeps it active. You can then connect to the terminal session whenever you need to using the docker exec command:
docker exec -it [CONTAINER_ID] bash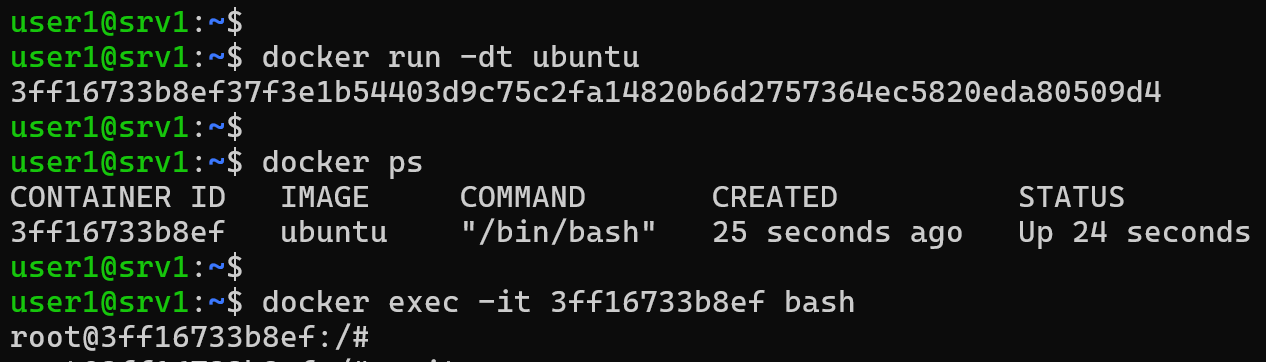
Why this is the best method
When you are finished, you can type exit. Because the container was started with -dt, your exit command only closes the terminal session, while the container remains running in the background.
Method 2: Interactive Mode and the Detach Sequence
Another method is to start the container in interactive mode. This automatically connects you to the terminal session as soon as the container is created.
The Command:
docker run -it ubuntuImportant: If you use the exit command here, the container will stop. To exit without stopping the container, you need to press Ctrl+P and then Ctrl+Q.
This key combination detaches your terminal but keeps the container active in the background.
Method 3: Docker Compose Configuration
If you use Docker Compose to manage your services, you can achieve the same result by adding a specific key to your docker-compose.yml file. You need to attach a pseudo-terminal using the tty key.
Example Configuration
services:
ubuntu-container:
image: ubuntu
tty: trueSetting tty: true ensures that Docker Compose keeps the container running in the background after it starts.
Summary and Next Steps
To recap, if you want to keep an Ubuntu container alive, you must provide a process or a terminal. Using docker run -dt is usually the most convenient method for most developers.
If you want to learn more about how to manage containers, make sure to read our tutorial on the docker run command. In that tutorial, we cover port mapping, which is an essential skill for any Docker user.