How to Set Up Remote Desktop on Linux Mint 22 Using XRDP
If you want to access your Linux Mint 22 computer remotely, one of the easiest ways to do that is by setting up Remote Desktop using XRDP. In this guide, I’ll show you step-by-step how to install and configure XRDP on Linux Mint 22, connect remotely, understand its limitations, and explore the best alternative if XRDP doesn’t work for you.
What Is XRDP in Linux Mint 22?
XRDP is an open-source implementation of Microsoft’s Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). It allows you to connect to your Linux Mint desktop from another computer using the built-in Remote Desktop Connection app on Windows or similar RDP clients.
Step 1: Install XRDP on Linux Mint 22
install XRDP using:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install xrdpOnce installed, check if the XRDP service is active and running:
systemctl status xrdpIf it says active (running), XRDP is now successfully installed. The enabled status means it will automatically start when your system boots.
Step 2: Network Configuration (Important)
The XRDP configuration files are located in the /etc/xrdp/ directory. The main file is called xrdp.ini.
Inside that file, you’ll find the port number (default: 3389) used for Remote Desktop connections.
- Firewall: If you have a firewall enabled, make sure to allow this port.
- External Access: If you want to access this computer from outside your home network, you have to configure port forwarding for this remote desktop port on your router.
- Public IP: Also, check with your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to make sure you have a public IP address directly assigned to your router — not a shared or CGNAT (Carrier-Grade NAT) IP. Without a public IP, external access won’t work.
Step 3: Connect to Linux Mint Remotely
After XRDP is installed and configured, you can connect from another computer using the IP address of your Linux Mint 22 system.
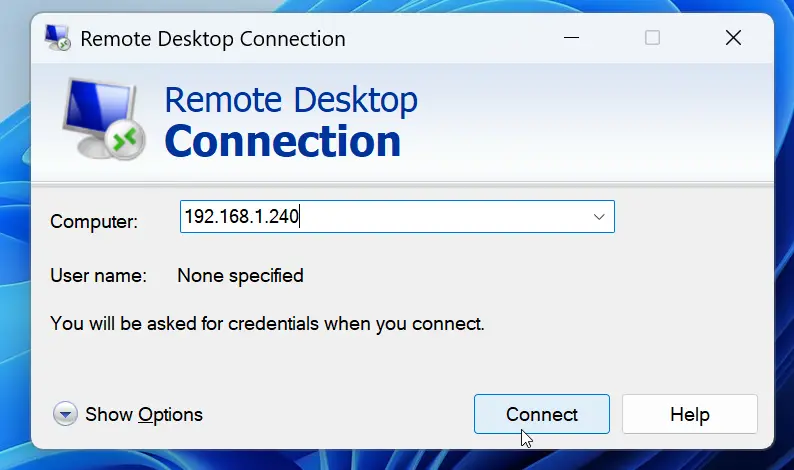
When you use a remote desktop connection tool (like the built-in Windows Remote Desktop Connection) and attempt to connect, you will be prompted for a login.
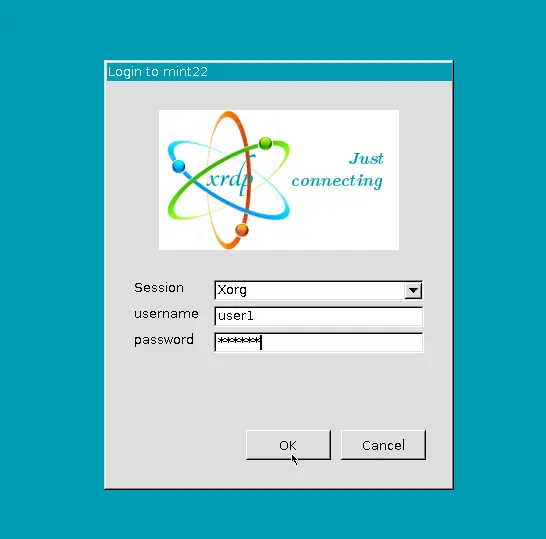
If the login screen appears, that means your Remote Desktop connection is working.
However, if your connection drops right after login, it’s because XRDP doesn’t allow logging in to both local and remote sessions using the same user account.
To fix this, simply log out from your local session first and then connect remotely.
Important Notes and Tips
- When you finish your remote session, always log out properly instead of closing the window. If you don’t, you may not be able to log in locally again without restarting your system.
- To avoid conflicts, create a second user account specifically for remote access. For example, create a user named user2.
Overcoming the Single-User Limitation
The most practical way to overcome the limitation of connecting both locally and remotely at the same time is to use two separate user accounts: one for local login and one for remote login.
After creating the user, make sure to log into that new account at least once locally. This is necessary because the desktop settings and configurations need to be set up properly, which happens only after an initial local login.
Limitations of XRDP on Linux Mint 22
While XRDP is a simple way to enable Remote Desktop, it has a few limitations:
- You can’t log into the same user account both locally and remotely at the same time.
- Port forwarding is required to access your computer from outside your home network.
Alternative Remote Desktop Software
If XRDP doesn’t work well for your setup, you can use Anydesk, a popular cross-platform remote desktop software for Linux, Windows, and macOS.
- Installation guide: How to Install Anydesk on Linux Mint 22
Conclusion
Setting up Remote Desktop on Linux Mint 22 using XRDP is a straightforward process. It allows you to access your desktop remotely, whether from another computer on your local network or over the internet with proper configuration.
If you need a simpler solution that works without port forwarding and supports simultaneous sessions, Anydesk is an excellent alternative.