How to Install Docker on Debian 12
In this guide, we’ll walk through how to install Docker on Debian 12 using the official installation script. We’ll also verify the installation by running a test container and configure Docker to run without using sudo.
Before You Start
Before downloading the script, make sure the curl command is installed on your system.
sudo apt update
sudo apt install curlInstall Docker
To install Docker on Debian 12, you just need to run the following three commands.
Uninstall any existing Docker packages:
for pkg in docker.io docker-doc docker-compose podman-docker containerd runc; do sudo apt-get remove $pkg; doneDownload the official Docker installation script:
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com -o get-docker.shRun the script to install Docker Engine:
sudo sh get-docker.shThe first command removes any existing Docker packages. The next two commands download the official Docker installation script and run it to install Docker Engine on your system.
At the end, you might see a suggestion to run a script to enable Docker rootless mode.
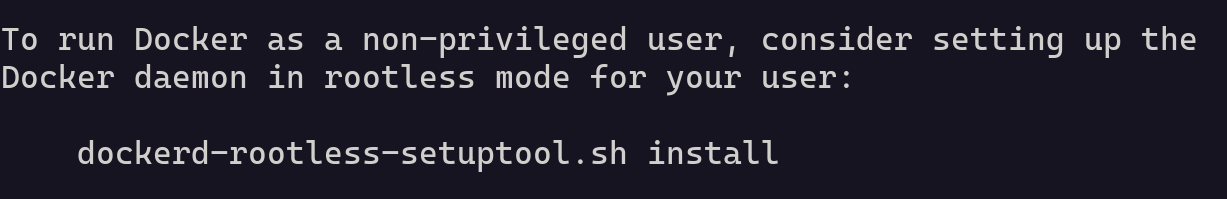
This allows Docker to run without root privileges, which can improve security in certain cases. But it’s something you can always do later if needed. For now, we don’t need to worry about it.
Verify the Installation
You can check the installed docker version by running the docker --version command.
sudo docker versionYou can also check the status of the Docker service using the systemctl status docker command. By default, the service is enabled to start automatically when the system boots.
systemctl status dockerRun Docker Without Sudo
By default you will have to use sudo every time we run a Docker command, which isn’t very convenient. To fix that, what you need to do is add your user to the Docker group.
sudo usermod -aG docker user_nameAfter adding the user to the Docker group, the change won’t take effect right away. So, you’ll need to restart the computer — for it to apply.
After the restart, you can run the groups command to verify that your user is now part of the Docker group. If you see "docker" listed, it means everything is set up correctly.
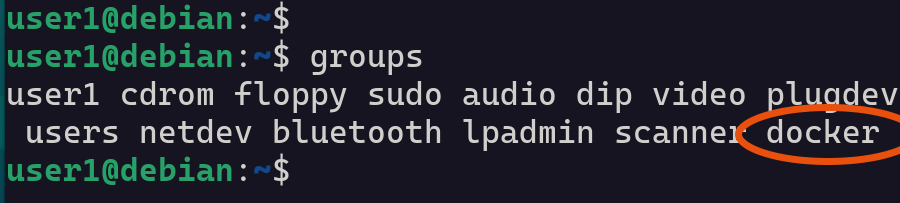
This lets you run Docker commands without needing sudo.
Run a Test Container
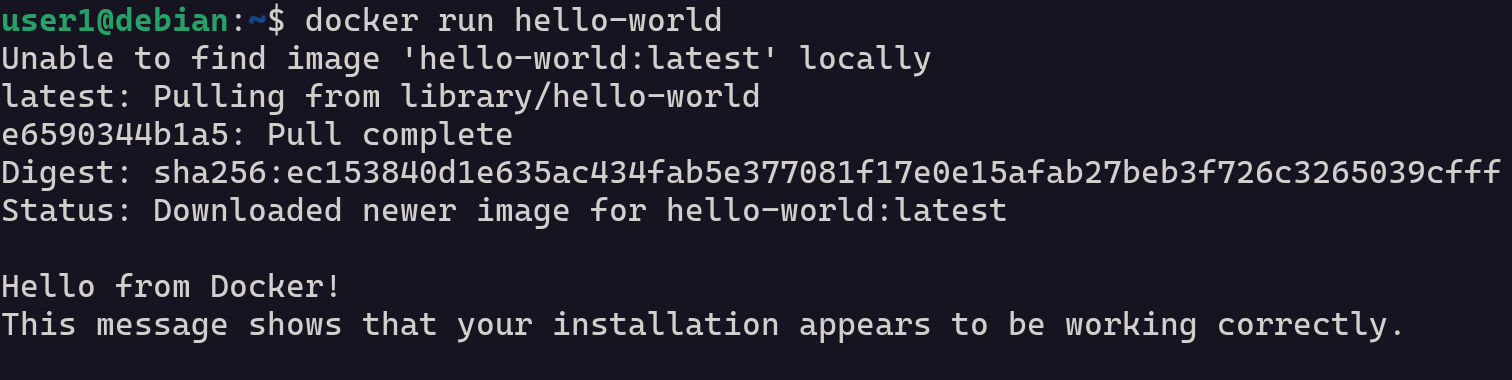
With our Docker setup complete, we’re now going to run a container called hello-world. It’s a lightweight test container designed to confirm that Docker is installed and working correctly.
docker run hello-worldWhen the command finishes, if you see the message "Hello from Docker!", that means your Docker installation was successful and everything is working as expected.
What’s Next
And now, you have Docker up and running on your Debian system. The next step is learning how to start containers using the docker run command.