How to Install Docker Engine on Fedora 43
This guide will walk you through the complete, step-by-step process of installing the Docker Engine on Fedora 43.
We will cover the installation commands, ensure the Docker service is running correctly, and, crucially, configure the docker command to run without sudo privileges. Finally, we will run a test container to confirm your Fedora Docker installation is successful.
Step 1: Install Docker Engine on Fedora 43
To install Docker on Fedora 43, you need to run three commands:
Command 1 (Uninstall any previous version):
sudo dnf remove docker docker-client docker-client-latest docker-common docker-latest docker-latest-logrotate docker-logrotate docker-selinux docker-engine-selinux docker-engineCommand 2 (Download Script):
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com -o get-docker.shCommand 3 (Run Installation):
sudo sh get-docker.sh- The first command will uninstall any previous or potentially conflicting Docker components, ensuring a clean Docker Engine installation environment.
- The second command downloads the official Docker installation script from the Docker website
- The third command runs the script to install Docker Engine.
After installation, you might see a message about Docker rootless mode. You can skip this step for now — it’s only required if you want to run the Docker daemon without root privileges.
Step 2: Start and Enable Docker Service
After installation, we must verify that the Docker service is running and configured to start automatically on system boot.
Check the status of Docker with:
sudo systemctl status dockerStart Docker: Start the Docker service immediately using the systemctl command.
sudo systemctl start dockerEnable Docker (Auto-start on boot): Use this command to set Docker to start automatically at the system reboot.
sudo systemctl enable docker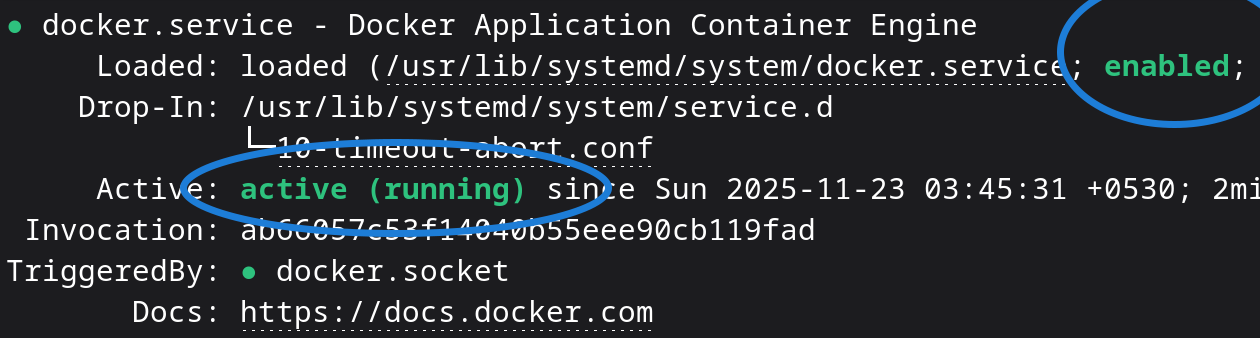
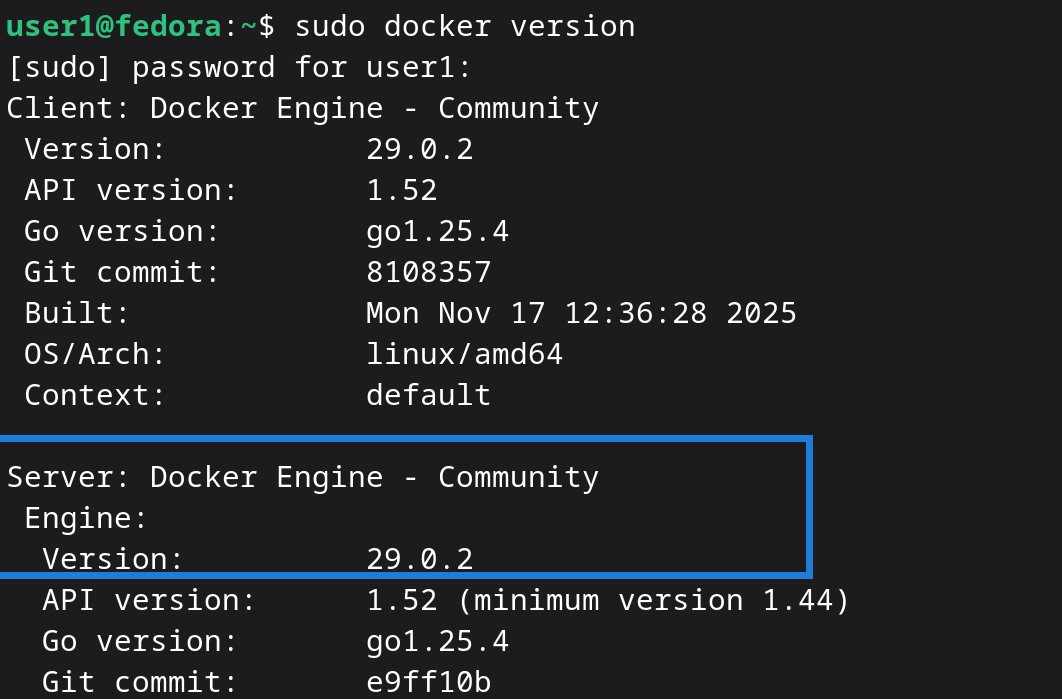
Now, run:
sudo docker versionYou should see your Docker Engine version displayed. This confirms Docker is installed and running successfully on Fedora 43.
Step 3: Run Docker Commands Without Sudo
By default, Docker requires root privileges. Running a Docker command without sudo will result in a permission denied error.
The next thing we are going to do is configure the docker command to run without sudo privileges. We achieve this by adding any user who needs to run Docker commands to the docker Linux group. Any member of this group can execute docker commands without needing sudo.
Add your user to the docker group. (Replace user_name with your actual username):
sudo gpasswd -a user_name dockerVerify the new group membership. Run the groups command:
groupsIf docker doesn’t appear in the list, restart your computer. After the restart, the user will be able to run Docker commands without sudo.
Step 4: Test Docker Installation by Running a Container
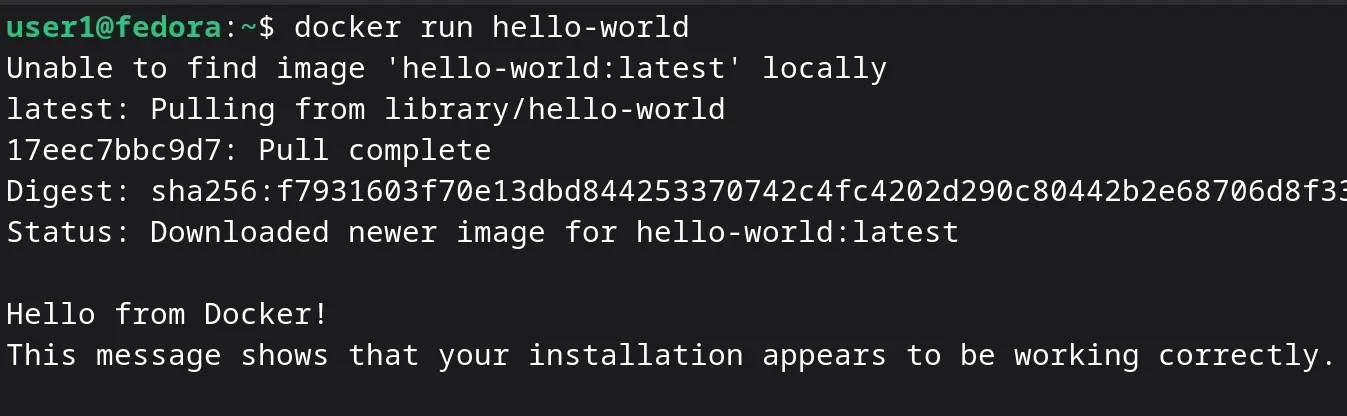
To verify your Docker installation, run the Hello World test container:
docker run hello-worldIf you see the message “Hello from Docker!”, your installation is successful. You are now ready to start running containers on Fedora 43 using Docker.
What Next
In the next tutorial, we will learn more about the docker run command and how to start containers in more detail.