How to Install Docker on Linux Mint 22
In this tutorial, we’ll look at how to install Docker on Linux Mint 22.
We’ll start by installing the Docker Engine, then configure the Docker command to run without using sudo privileges. Finally, we’ll run a test container to confirm that Docker is installed correctly and everything is working.
Install Docker Engine on Linux Mint 22
To install Docker on Linux Mint 22, you need to run three commands.
Uninstall any previous Docker versions:
for pkg in docker-ce docker-ce-cli docker-desktop docker-model-plugin containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin docker-ce-rootless-extras docker.io docker-doc docker-compose docker-compose-v2 podman-docker containerd runc; do sudo apt-get purge -y $pkg; doneDownload the Installation Script:
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com -o get-docker.shRuns the script to install Docker Engine:
sudo sh get-docker.shThe installation is finished.
- The first command is optional — it removes any previous Docker versions on your system.
- The second command downloads the official Docker installation script from Docker’s website.
- The third command runs the script to install Docker Engine.
Checking the Installation
At the end of the installation process, you may see a message suggesting a script to set Docker in "rootless mode." This is an extra security step that configures Docker Engine to run without root privileges, but it is optional and something you can do later.
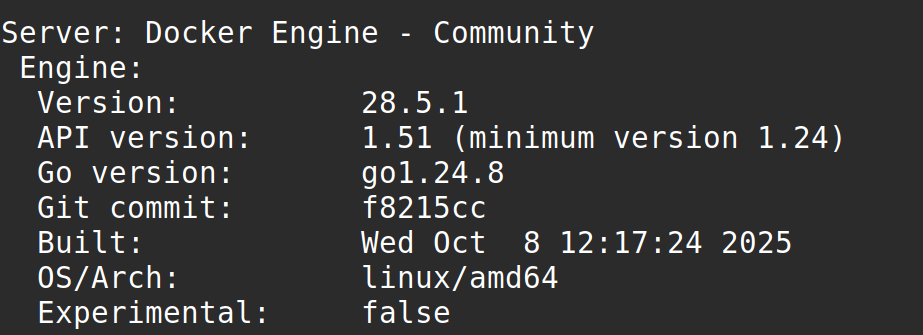
For now, let us run the docker version command to check the Docker version installed on the computer:
docker versionThis output should confirm the Docker Engine version installed on your Linux Mint system.
Configure Docker to Run Without sudo
By default, you need sudo privileges to execute Docker commands. To avoid typing sudo every time, add your user to the docker group.
If you look inside the /etc/group file, you’ll find a group called docker. Any user who belongs to this group can run Docker commands without sudo.
To add your user to the group, run:
sudo gpasswd -a <username> dockerFor example:
sudo gpasswd -a user1 dockerCheck if the user was added to the group:
groupsIf docker doesn’t appear in the list yet, restart your computer to apply the change.
After restarting, run groups again — now you should see docker listed. That means you can run Docker commands without sudo.

Test Docker Installation
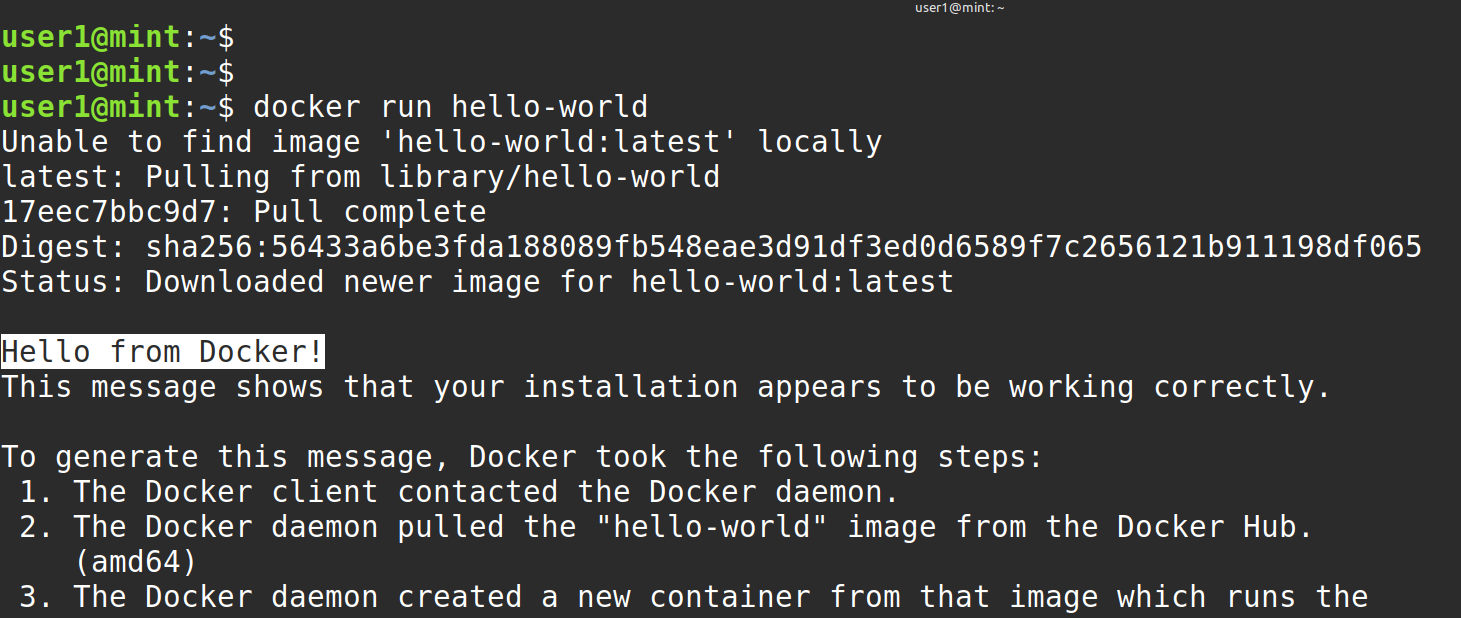
The final step is to run a simple container to fully test your installation. We will start a new container called hello-world.
Run the following command:
docker run hello-worldIf you see the message “Hello from Docker”, it means your installation is successful.
What’s Next
Now that Docker is installed and working, the next step is to learn how to run containers using the docker run command.
In the next tutorial, we’ll go through the docker run command in detail — how it works, different options you can use, and how to start, stop, and manage containers efficiently.
Next Tutorial: Learn the Docker Run Command Explained Step by Step